Modern agriculture is undergoing a profound transformation, driven by technological advancements that are making farming practices more efficient, productive, and sustainable than ever before.Among all exciting innovations, Global Navigation Satellite Systems (GNSS) have emerged as a cornerstone technology, revolutionizing the way modern farmers manage their operations.
Then, what does GNSS stand for in modern farming, and how can you take full advantage of the GNSS technology? In this article, CHCNAV will guide you through all to explore how GNSS enables unprecedented accuracy and automation in the field!

What Does GNSS Stand For?
1. What is GNSS?
GNSS stands for Global Navigation Satellite System. It is an umbrella term that encompasses all satellite systems providing positioning, navigation, and timing (PNT) services on a global or regional basis.Think of it as the infrastructure that allows receivers on the ground - like those in your smartphone or advanced farming machinery - to determine their precise location, velocity, and time by processing signals broadcast from a constellation of orbiting satellites.
2. Four Global GNSS Constellations
Currently, there are four fully operational global GNSS constellations, each managed by a different nation or entity:
- Galileo (European Union): This European system offers high-precision positioning services and is known for its robust signal and independent control.
- GPS (Global Positioning System) (United States): The most widely recognized GNSS, GPS has been operational for decades and is applied in different industries to provide reliable positioning worldwide, such as agricultural GPS systems.
- GLONASS (Globalnaya Navigatsionnaya Sputnikovaya Sistema) (Russia): This Russian system offers a global alternative for satellite-based positioning.
- BeiDou (China): Rapidly expanding, BeiDou provides global coverage and incorporates unique features like short message service capabilities.
These global systems ensure that virtually any point on Earth has access to signals from multiple satellites, enabling accurate positioning.
Key Applications of GNSS in Modern Farming
The integration of GNSS technology has been a cornerstone in the development and widespread adoption of precision agriculture. This modern farming approach utilizes data and technology to optimize every stage of the crop production cycle, maximizing yields while minimizing inputs and environmental impact.
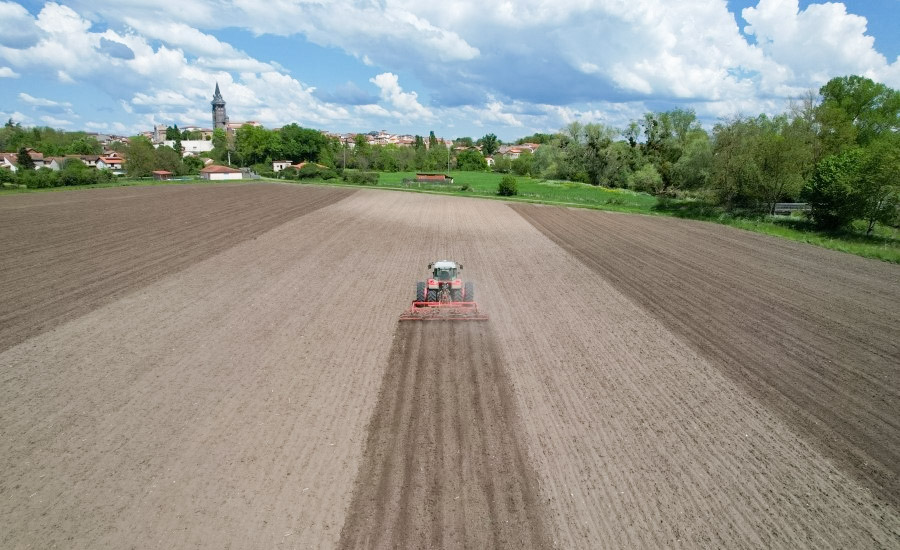
One of the most significant achievements of GNSS in agriculture is the enablement of automated steering and guidance. GNSS-enabled auto-steering systems for tractors, harvesters, and other machinery allow for highly accurate and consistent passes in the field. This eliminates overlaps and skips, ensuring that every section of the land is treated correctly during planting, spraying, and harvesting.
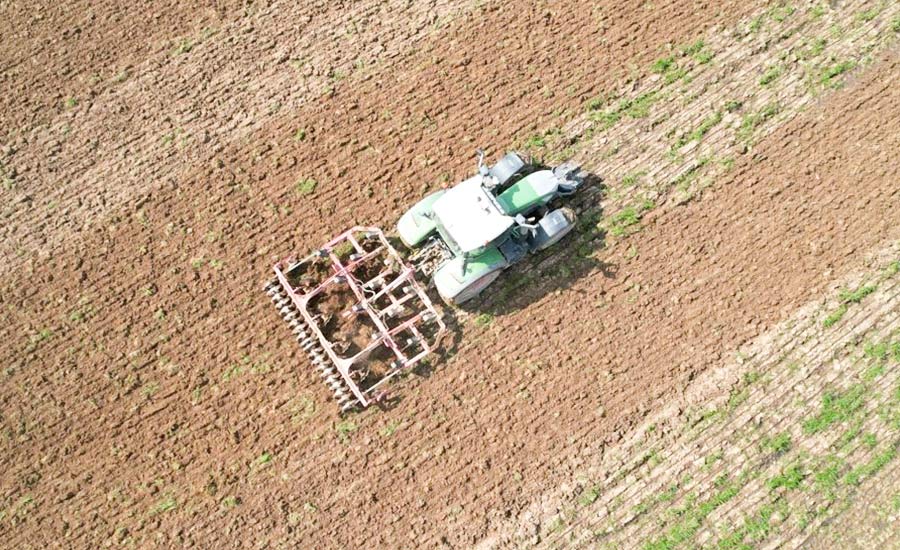

Furthermore, this technology can achieve an impressive accuracy of down to 2.5 centimeters, a benchmark that leading manufacturers (like CHCNAV) in the industry have reached. This level of precision is currently considered the upper limit within the existing technological framework.
Advantages of Using GNSS in Farming
The adoption of GNSS technology brings a wealth of benefits to modern farming practices:
1.Increased Efficiency
GNSS technology significantly streamlines farming operations. Automated machinery guided by GNSS can maximize time utilization through 24/7 operation and function effectively in low-visibility weather. They can operate at consistent speeds, increasing the overall efficiency of field operations.
The high positioning accuracy also saves fuel by reducing overlaps and improves land utilization by minimizing missed areas. Additionally, precise application of inputs such as seeds, fertilizers, and pesticides minimizes waste and optimizes resource use.
2.Improved Crop Management
GNSS enables high-precision data that helps better decision-making, from planting to harvesting. For example, precise planting ensures optimal plant spacing, which in turn enhances resource efficiency and boosts crop yields. Moreover, GNSS-guided spraying allows for the precise application of pesticides and herbicides, minimizing off-target drift and environmental impact.
3.Environmental Benefits
By optimizing the use of inputs and reducing waste, GNSS contributes to more sustainable farming practices. Precise application of fertilizers and pesticides helps minimize runoff and lower the risk of soil and water contamination. Additionally, efficient machinery operation reduces fuel consumption and greenhouse gas emissions, further enhancing the environmental benefits of GNSS in agriculture.
The cumulative effect of these advantages translates into significant economic benefits for farmers. The combination of lower costs (through reduced consumption of seeds, fertilizers, pesticides, and fuel) and higher yields (through optimized resource allocation and precise operations) directly boosts farm profitability!
Challenges of Using GNSS in Agriculture
While the benefits of GNSS in agriculture are substantial, challenges also emerge when associated with its adoption:
1.Initial Investment Costs
The initial investment in GNSS-equipped machinery, software, and correction services can be significant, representing a barrier for some farmers, particularly smaller operations. The good news is that many farmers find that the upfront costs are justified by the long-term benefits.
2.Signal Interference
Additionally, it should be noted that various factors, including atmospheric conditions, terrain, and man-made structures, can affect GNSS signals. These factors can compromise signal integrity, thereby reducing the accuracy and reliability of positioning data.
However, advanced correction techniques such as Differential GNSS (DGNSS), Real-Time Kinematic (RTK), and Precise Point Positioning (PPP) can enhance signal accuracy and mitigate these issues.
3.Technical Expertise
Plus, effectively utilizing GNSS technology requires a certain level of technical expertise. You or your staff need to understand how to operate the equipment, interpret the data, and integrate it into your farm management practices. This often involves knowledge of Geographic Information Systems (GIS), remote sensing, and other related technologies.
However, modern GNSS products, such as those from CHCNAV, are designed with intuitive interfaces that simplify even complex professional operations, making them easy to learn and use. Furthermore, you won't have to navigate technical challenges alone. Our local dealers and the dedicated CHCNAV technical team provide comprehensive support, ensuring you can use the equipment smoothly and efficiently.
Let CHCNAV Empower Your Precision Agriculture Practices!
CHC Navigation (CHCNAV) is a global leader in providing innovative GNSS solutions for various industries, including agriculture. With a strong focus on research and development, we offer a comprehensive range of products and services aiming to empower modern farmers. Some of our offerings include:
- Automated Steering Systems: Such as the NX612, NX510 SE, and NX510 Pro, which deliver ±2.5 cm auto-steering accuracy for tractors and other machinery.
-
GNSS Base Stations: Like the iBase AG, which provides reference data for RTK corrections and high-precision operations.
-
Land Leveling and Manual Guidance Systems: Enhancing efficiency for a range of field tasks.
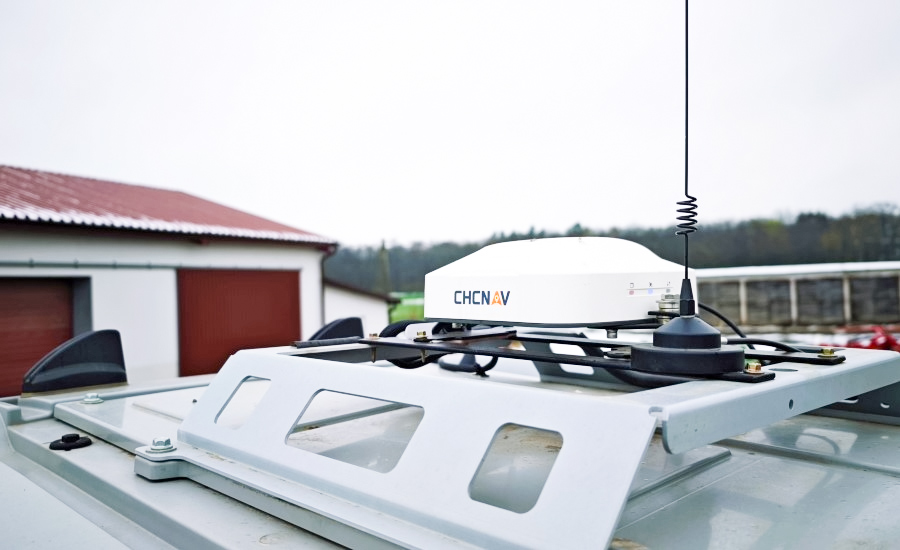

They are designed for ease of use, compatibility with different machinery, and support for all major GNSS constellations, ensuring robust performance even in challenging environments.These systems have been widely adopted for tasks like automated planting, spraying, and harvesting, helping global farmers boost yields and profitability with cutting-edge technology.
Conclusion
What does GNSS stand for in modern farming practices? It has become the foundation of modern, efficient, and sustainable agriculture. By enabling automation and precision farming, agricultural GNSS systems help farmers increase yields, reduce costs, and protect the environment.
CHCNAV is at the forefront of this transformation, offering a comprehensive suite of GNSS-enabled products and solutions tailored for modern farming. Feel free to contact us to learn more about how CHCNAV can help you harness the power of GNSS for your farm. The future of farming is here—and it's guided by GNSS.
FAQs About GNSS
1.Are GPS and GNSS the same?
No, GPS and GNSS are not the same. GPS (Global Positioning System) is one of several GNSS constellations. GNSS is the umbrella term for all satellite navigation systems, including GPS, GLONASS, Galileo, BeiDou, and regional systems like QZSS and IRNSS.
2.How many GNSS satellites are there?
The number of GNSS satellites varies by system and time. For now, the GPS constellation consists of approximately 31 operational satellites, while Galileo has 27, GLONASS has 24, and BeiDou has about 45. Additionally, regional systems like QZSS and IRNSS have their own satellite constellations.
3.Which GNSS is most accurate today?
The accuracy of GNSS depends on various factors, including the receiver quality, the number of satellites in view, atmospheric conditions, and the use of augmentation systems like RTK or PPP. Under ideal conditions and with the use of correction services, most modern GNSS systems can achieve similar levels of high accuracy, reaching up to ±2.5 cm accuracy. This is also the current industry standard for automated agricultural machinery.
The choice of which system to rely on often depends on factors like signal availability in a specific location and the compatibility of the receiver. Often, receivers utilize signals from multiple GNSS constellations simultaneously to enhance accuracy and reliability.
____
About CHC Navigation
CHC Navigation (CHCNAV) develops advanced mapping, navigation and positioning solutions designed to increase productivity and efficiency. Serving industries such as geospatial, agriculture, construction and autonomy, CHCNAV delivers innovative technologies that empower professionals and drive industry advancement. With a global presence spanning over 140 countries and a team of more than 2,000 professionals, CHC Navigation is recognized as a leader in the geospatial industry and beyond. For more information about CHC Navigation [Huace:300627.SZ], please visit: www.chcnav.com