Agriculture has always been a field where innovation meets tradition. The recent technological advances bring about exciting, groundbreaking changes in boosting efficiency and productivity.Among all, the adoption of GPS in agriculture revolutionizes farming practices. It sets the stage for smarter, more efficient farming methods, like precise field mapping, automated machinery guidance, and real-time data analytics.
As a professional in auto steering system solutions for precision farming, CHCNAV will guide you through the relationship between GPS and agriculture, that is, what GPS is and how GPS works to transform the agricultural landscape.
GPS is one of the GNSS constellations.
What is GPS?
GPS (Global Positioning System) is the first fully operational Global Navigation Satellite System (GNSS). This U.S. government satellite-based navigation technology provides location data and time information.Started in the 1980s, GPS was available for civilian uses and gradually became an essential tool in countless industries, including agriculture.
How Does GPS Work?
The working principle of GPS is similar to that of other GNSS systems, all of which include a space segment, a control segment, and a user segment.
1. Space Segment
The space segment of GNSS includes constellations of satellites orbiting the Earth. For example, the GPS constellation has over 30 satellites at an altitude of about 11,000 miles. These satellites broadcast one-way navigation signals that indicate the precise location and time of the satellite.
2. Control Segment
The control segment of GNSS is made up of Earth-based stations for satellite monitoring and control. These stations track the satellites, send command maneuvers to maintain their orbits, and monitor data transmissions. For GPS, the control segment is developed, maintained, and operated by the U.S. Space Force.
3. User Segment
The user segment of GNSS consists of receiver equipment or devices, such as watches and smartphones. These receivers capture and decode the transmitted signals from the satellites to calculate the user's position and time. For instance, a receiver can compute three-dimensional positions (latitude, longitude, and altitude) and time by combining signals from at least four satellites.
Applications of GNSS Technology
GNSS technology, which includes systems like GPS, has found wide and versatile applications in navigation, logistics, disaster management, construction, and, of course, agriculture. More importantly, these systems drive development across all sectors when enhanced with technologies like Differential GPS (DGPS) and Real-Time Kinematic (RTK) positioning.
How is GNSS Used in Agriculture?
The use of GNSS in agriculture has opened up a world of possibilities for farmers. From improving crop yields to reducing environmental impact, here are some of the key applications of GNSS in agriculture:
- Field Mapping and Soil Sampling
GNSS enables farmers to create detailed field maps that illustrate soil composition, crop performance, and irrigation needs. By combining GNSS data with Geographic Information Systems (GIS), farmers can identify which areas of a field require specific treatments. Soil sampling becomes far more systematic and accurate, allowing for targeted interventions, such as customized fertilizer applications.
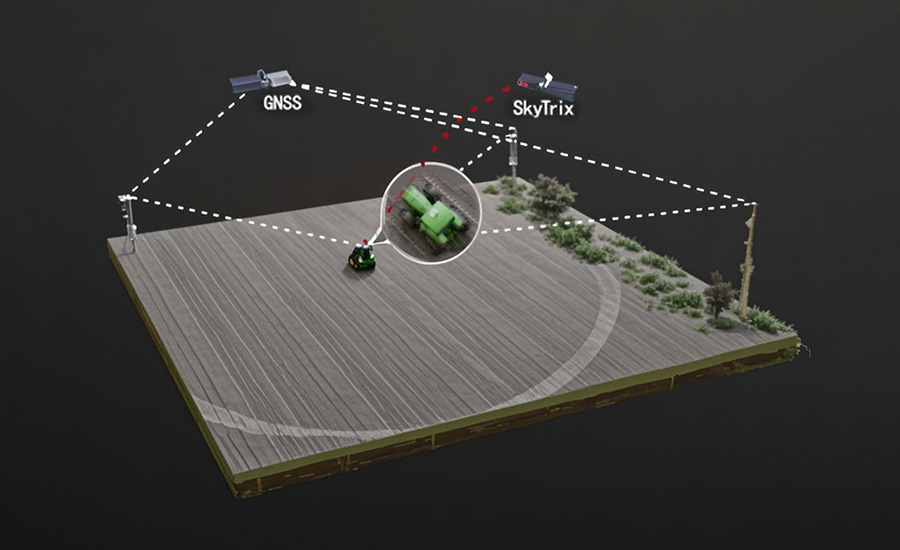
GNSS technology in agriculture guides tractors, planters, and other agricultural machinery with precision, especially when enhanced with techniques like RTK. Automated systems embedded in machinery can follow pre-programmed paths across a field, ensuring uniform coverage and reducing overlaps. This not only saves time but also reduces fuel consumption and wear on equipment.
- Precision Planting and Crop Management
With GNSS in agriculture, farmers can ensure seeds are planted at the optimal spacing. Similarly, GNSS-enabled crop management systems monitor variables like plant health, pest activity, and water stress in real time. These insights enable precise intervention, minimizing resources while maximizing yield.
GNSS data works hand in hand with sensors to optimize irrigation systems. Farmers can identify areas with varying water needs and adjust irrigation patterns accordingly. This leads to more efficient water use, promoting sustainable farming practices.
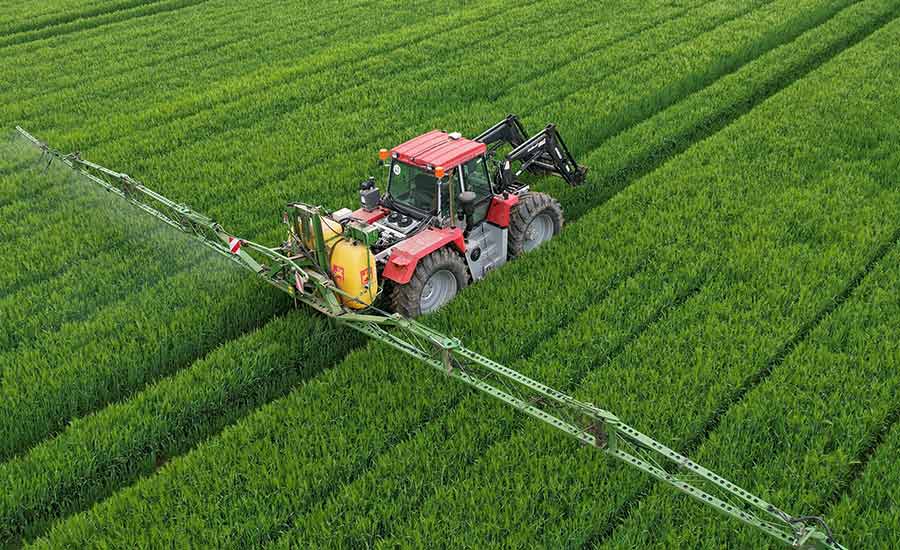

GNSS For Irrigation Management
- Livestock Tracking and Management
GNSS tracking systems also enable farmers to attain the location and movement information of livestock, enhancing safety and ensuring efficient grazing practices. GNSS collars and ear tags make it easy to track animals across large pastures.
- Real-Time Monitoring and Decision-Making
GNSS-compatible software and IoT devices provide farmers with real-time updates on weather, soil moisture, and equipment performance. These insights allow for swift, informed decisions to address urgent issues, such as unexpected pest outbreaks or machinery malfunctions.
Benefits of GNSS in Agriculture
GNSS technology in agriculture has opened up new possibilities for farmers. From improving crop yields to reducing environmental impact, here are some of the key benefits of GNSS in agriculture:
- Enhanced Operational Precision
GNSS typically facilitates meter-level accuracy, and the accuracy can be improved to centimeter-level when integrated with advanced techniques like DGPS and RTK. This precision minimizes errors during planting, fertilizing, and harvesting, ensuring that every resource is used optimally.
By automating repetitive tasks and reducing inefficiencies, GNSS technology allows farmers to cover larger areas in less time. This scalability supports higher productivity, even in small-scale farms.
- Resource Optimization and Cost Savings
Precise mapping and targeted applications help reduce the use of seeds, fertilizers, pesticides, and water. This leads to significant input cost reductions while minimizing environmental impact.
- Data-Driven Decision-Making
GNSS technology in agriculture generates valuable data that provides actionable insights. Farmers can analyze historical trends and predict future outcomes, improving planning and risk management.
- Intelligent Agricultural Machinery Management
GNSS empowers the next generation of autonomous agricultural machinery. Equipment can operate with minimal human intervention, reducing labor costs and human errors.
- Environmental Sustainability
Precision farming techniques supported by GNSS technology minimize waste and reduce the overuse of chemicals. This keeps soil and water resources healthier for future generations.
CHCNAV's Leading Positioning Solutions for Precision Farming
CHC Navigation (CHCNAV) is one key player in offering comprehensive solutions designed specifically for precision agriculture. Our product catalog includes:
- Auto steering systems that achieve cm-level accuracy and are suitable for diverse uses.
- Manual guidance systems that are ideal for different field conditions and support upgrades.
- Land leveling systems with built-in GNSS RTK for improved precision and efficiency.
- GNSS systems that transmit reliable signals for accurate positioning data.

CHCNAV NX612 Automated Steering System
They aim to boost productivity and sustainability for modern farming and take our CHCNAV NX612 Automated Steering System as an example:
This auto-steering system is compatible with major GNSS systems, including GPS, BDS, GLONASS, Galileo, and QZSS. Additionally, its performance is enhanced by supporting techniques like SPP, DGPS, RTK, E-PPP, H-PPP, and SkyTrix. The improved cm-level accuracy can be beneficial to diverse farming practices, such as precision seeding, strip cropping, crop spraying, and optimizing the harvesting process.
FAQs About GNSS And GPS in Agriculture
1. What is the difference between GNSS and GPS in agriculture?
GPS is one type of Global Navigation Satellite System (GNSS). GNSS includes GPS (USA), GLONASS (Russia), Galileo (EU), and BeiDou (China). While GPS is commonly used, GNSS-enabled devices can utilize multiple satellite constellations, improving accuracy and reliability. For agriculture, GNSS systems provide enhanced precision and dependability, especially in areas where GPS signals might be obstructed or weak.
2. What is the future of GNSS technology in agriculture?
The future of GNSS in agriculture revolves around increased automation and data integration. Autonomous vehicles, drone technology, and AI-driven analytics will work in unison with GNSS systems. Next-generation technologies like 5G connectivity and cloud computing will allow for real-time, large-scale farming operations that are more precise and environmentally friendly.
3. What types of agricultural equipment use GNSS for precision farming?
A wide variety of equipment now integrates GNSS technology to improve farming efficiency, including:
- Tractors (for automation and guidance)
- Planters and seed drills
- Sprayers and spreaders
- Combine harvesters
- Irrigation controllers
- Livestock trackers
These tools showcase the seamless adoption of GNSS across all stages of agricultural production.
Conclusion
GNSS technology, including GPS, has fundamentally changed how we grow food and manage resources in agriculture. By offering precision, time savings, and sustainability, GNSS has become an indispensable tool for modern farmers. From field mapping and machinery guidance to real-time data analysis, it supports every aspect of farming.
For those seeking to integrate the power of GNSS into their operations, CHCNAV stands as a trusted provider of top-tier solutions. Our innovative products ensure that farmers achieve higher yields while protecting the environment. Contact CHCNAV for more details on how we can help you step toward smarter farming. We deliver reliable, innovative tools for modern farming needs!
____
About CHC Navigation
CHC Navigation (CHCNAV) develops advanced mapping, navigation and positioning solutions designed to increase productivity and efficiency. Serving industries such as geospatial, agriculture, construction and autonomy, CHCNAV delivers innovative technologies that empower professionals and drive industry advancement. With a global presence spanning over 140 countries and a team of more than 2,000 professionals, CHC Navigation is recognized as a leader in the geospatial industry and beyond. For more information about CHC Navigation [Huace:300627.SZ], please visit: www.chcnav.com